While melatonin is known for helping people reset their circadian rhythms for restorative sleep, there’s growing evidence that this natural hormone fights bacteria, inhibits viral infections, and even prevents the spread of cancer.
So even though melatonin is commonly known, it has many amazing attributes that can help restore and preserve your health in many ways. I’d like to review a few of them here, but suffice to say, boosting your melatonin levels may be one of the most important things you can do for a long and happy life.
Strong Immune System: Stop Bacterial and Viral Invaders
 Melatonin provides a baseline of protection all the time against the usual germs, bacteria, and viruses that we are likely to encounter on a regular basis.
Melatonin provides a baseline of protection all the time against the usual germs, bacteria, and viruses that we are likely to encounter on a regular basis.This amazing nutrient appears to moderate the immune response quite well, keeping it strong. This is why researchers are recommending its use in Europe to help treat and modulate dangerous viruses, including COVID-19.
Melatonin is also a vital concern for older individuals, who typically have lower levels of the hormone, and an overall decline in antibodies. This is most likely one of the major reasons why viruses can attack the elderly—their overall immune system is already compromised, and a lack of melatonin is part of that.
Melatonin is one of the most important and most underappreciated components of a strong immune system. If you want to thrive during a time of intense challenges, melatonin supplementation is a must.
Prevent Cancer
 Melatonin is present virtually everywhere in the human body. It is found in the brain, retina, skin, gastrointestinal tract, thyroid, liver, kidneys, immune system cells, endothelial cells, and reproductive organs. It is also present in spinal fluid, saliva, bile, breast milk—often in higher concentrations than it is in the blood.
Melatonin is present virtually everywhere in the human body. It is found in the brain, retina, skin, gastrointestinal tract, thyroid, liver, kidneys, immune system cells, endothelial cells, and reproductive organs. It is also present in spinal fluid, saliva, bile, breast milk—often in higher concentrations than it is in the blood.Because melatonin is interwoven in virtually every action, cell, and process in the body, including antioxidant protection, anti-inflammatory responses, and genetic replication, it has an essential role in cancer. Melatonin prevents free radical and inflammatory damage to DNA and inhibits the abnormal cellular replication that creates cancerous tumors in the first place.
Scientific research shows that the presence of melatonin inhibits cancer in many ways. While we sleep, our cells rely on melatonin to maintain homeostasis. That’s just a fancy way of saying that melatonin keeps our systems on an even keel. That may sound basic, but small disruptions—including a lack of melatonin in our cells, or a lack of opportunity for the body to create melatonin—make it easier for damaged cells to replicate.
Without proper levels of melatonin on board to maintain the various checkpoints along the way, these damaged cells can get out of control and form tumors. This is one of the reasons why people who work night shift may be more susceptible to cancer, especially breast cancer. Their circadian rhythms are thrown off too much and for too long.
But if tumors develop and cancer treatment becomes necessary, it’s not too late to employ melatonin. That’s because melatonin makes cancers less resistant to anticancer drugs, which is good news for those undergoing conventional cancer treatments.
Treat Depression
 Our state of mind is directly related to circadian rhythms. Clinical work has found that by synchronizing those rhythms through treatment with melatonin, people can feel some relief from the symptoms of depression. But that’s not the only way that melatonin can prevent or alleviate depression and anxiety, and strengthen other aspects of mood and well-being.
Our state of mind is directly related to circadian rhythms. Clinical work has found that by synchronizing those rhythms through treatment with melatonin, people can feel some relief from the symptoms of depression. But that’s not the only way that melatonin can prevent or alleviate depression and anxiety, and strengthen other aspects of mood and well-being.Melatonin is one important component in that big picture, and can actually help change the way the brain is structured and how it learns new habits and emotional responses. In scientific terms, this is known as neuroplasticity—the ability of the brain to change, grow, and develop.
In some cases, there are variations in genes that reduce levels of natural melatonin production in the body. It’s been found that those with major depressive disorder (MDD) have lower plasma levels of melatonin.
Prevent Cognitive and Neurological Conditions
 The boost in neuroplasticity from melatonin also makes it a compelling option for individuals with cognitive and neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease (AD) or Parkinson’s. Melatonin can also inhibit the buildup of beta-amyloid plaque in the brain, associated with Alzheimer’s.
The boost in neuroplasticity from melatonin also makes it a compelling option for individuals with cognitive and neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease (AD) or Parkinson’s. Melatonin can also inhibit the buildup of beta-amyloid plaque in the brain, associated with Alzheimer’s.And there is a relationship between lack of sleep and neurodegeneration. It’s not just about whether you feel groggy in the morning —your brain needs restorative sleep in order to function. It’s been estimated that 63 percent of adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and about 44 percent of those with Alzheimer’s have significantly interrupted or disturbed sleep.
Some clinical work has shown that even low doses of prolonged-release melatonin can improve cognitive function and memory in those with AD when it’s been added on to their existing standard treatment. Therefore, melatonin might not only slow the outward signs of disease progression, it is also safe to use with other medications.
Other research that has focused on Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, autism spectrum disorder, multiple sclerosis, and other conditions has seen similar results: melatonin and circadian cycle is deeply entwined with the severity of symptoms.
Treat GERD, IBS, and Other Digestive Disorders
 Scientific research has shown that melatonin protects the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, preserving it from ulcerative damage. Other clinical work has examined the results of melatonin for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Researchers found that melatonin relieved gastric pain and heartburn.
Scientific research has shown that melatonin protects the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, preserving it from ulcerative damage. Other clinical work has examined the results of melatonin for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Researchers found that melatonin relieved gastric pain and heartburn.Likewise, melatonin levels may be a deciding factor for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) treatment. A clinical study found that 8 mg of melatonin per day significantly improved symptoms. In this case, researchers noted that melatonin has a relaxing effect on the smooth muscle of the digestive system.
Other clinical research has found that melatonin treatment, due to its immune-modulating and anti-inflammatory effects, may have strong therapeutic effects and prevent flare-ups of ulcerative colitis (UC). Patients in this study taking melatonin had lower intensity in depression and anxiety symptoms as well, which is no doubt also related to UC symptom remission.
Prevent and Treat Autoimmune Diseases
 Autoimmune diseases are especially difficult to treat because they involve an upset in the balance of the very system that is designed to protect us from harm. Autoimmune conditions can affect the skin, joints, digestion, and left to their own, they cause permanent damage.
Autoimmune diseases are especially difficult to treat because they involve an upset in the balance of the very system that is designed to protect us from harm. Autoimmune conditions can affect the skin, joints, digestion, and left to their own, they cause permanent damage.Fortunately, melatonin may provide a natural intervention for autoimmune conditions, helping restore and modulate the immune responses that create havoc.
Research has shown that melatonin controls the release of natural immune compounds and T-cell responses. Much in the same way that melatonin can help stop the overexpression of cytokines for those with viral infections, it can also inhibit the actions of TNF-a through the NF-kB pathway, preventing the inflammatory symptoms seen in ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, inflammatory bowel disease, and multiple sclerosis.
Protect Your Heart
 Cardio health, including blood pressure, lipid levels, heart muscle strength, and vascular integrity are all tied to melatonin levels. In fact, continual light is a major risk factor for heart disease because of the way it depletes melatonin. So while it’s healthy to get outside in the summertime for plenty of exercise and fresh air, it’s equally important to reclaim your nighttime and keep lights to a minimum in the evening. We need darkness to stay healthy!
Cardio health, including blood pressure, lipid levels, heart muscle strength, and vascular integrity are all tied to melatonin levels. In fact, continual light is a major risk factor for heart disease because of the way it depletes melatonin. So while it’s healthy to get outside in the summertime for plenty of exercise and fresh air, it’s equally important to reclaim your nighttime and keep lights to a minimum in the evening. We need darkness to stay healthy!Studies have found that melatonin lowers blood pressure levels, reduces LDL cholesterol, and restores the health of blood vessels, in part, by normalizing nitric oxide levels and decreasing the reactivity and oxidative stress in arteries and veins.
Control Blood Sugar Levels, and Reduce Risk of Metabolic Syndrome
 As for blood sugar control and addressing type 2 diabetes (another epidemic of our times), melatonin and insulin levels are deeply connected. Melatonin is so effective at stopping inflammation and free radical damage, it can prevent or treat retinal neuropathy and other nerve and blood vessel damage associated with out-of-control glucose levels.
As for blood sugar control and addressing type 2 diabetes (another epidemic of our times), melatonin and insulin levels are deeply connected. Melatonin is so effective at stopping inflammation and free radical damage, it can prevent or treat retinal neuropathy and other nerve and blood vessel damage associated with out-of-control glucose levels.Individuals who are more at risk of type 2 diabetes may have altered MT2 (melatonin) receptors that are involved with non-rapid eye movement (REM) sleep—the deeper restorative sleep needed by the mind and body for proper repair and function. Additionally, the nature of circadian rhythms and blood sugar are intimately tied to our perceived need for caloric intake that changes with day and light cycles. Melatonin also helps protect pancreatic cells, which are susceptible to oxidative damage.
Restore and Preserve the Liver
 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is estimated to affect about one third of people living in industrialized countries. Extra fat deposits in the liver are serious. They threaten the liver’s ability to filter blood, detoxify harmful substances, metabolize drugs, and properly digest food due to decreased bile production.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is estimated to affect about one third of people living in industrialized countries. Extra fat deposits in the liver are serious. They threaten the liver’s ability to filter blood, detoxify harmful substances, metabolize drugs, and properly digest food due to decreased bile production.When it comes to liver protection, melatonin also plays an important role. In a clinical study of individuals with NAFLD, 10 mg of melatonin (5 mg, twice daily) significantly reduced triglyceride and LDL cholesterol, improved fat metabolism in the liver, and lowered inflammatory cytokine levels.
Melatonin also fights cirrhosis by preventing or inhibiting liver cell death, and stopping liver inflammation. Melatonin inhibits macrophage, mast cell, and leucocyte activity implicated in cases of liver fibrosis.
Manage Menopause and Healthy Aging
 While estrogen, phytoestrogens, and botanicals like black cohosh and rhodiola are some of the first things that come to mind for dealing with menopause symptoms, there is growing research that shows that melatonin may be an important addition.
While estrogen, phytoestrogens, and botanicals like black cohosh and rhodiola are some of the first things that come to mind for dealing with menopause symptoms, there is growing research that shows that melatonin may be an important addition.In one clinical study, postmenopausal women who had experienced weight gain also had lower levels of melatonin. Since melatonin tends to help slow weight gain, researchers believe it’s because of its inhibition on appetite-stimulating digestive enzymes and acids. And, while low levels of estrogen can be a factor in weight, melatonin levels appear to be just as important. Melatonin supplementation could be an effective alternative for women who have difficulty tolerating hormone therapy.
For those in perimenopause, a clinical study of women ages 45-54 found that melatonin can improve symptoms, reduce menstrual cycling, and lengthen the time between menstrual cycles. Plus, melatonin helps prevent bone loss, a common occurrence— especially for women—as they get older.
Experience Restorative Sleep
Melatonin is best known for the way it supports healthy sleep cycles. Natural melatonin production is considerably reduced when light strikes the retina of the eye. If you stay up late watching television or using smart phones, tablets, or computers, you’re interrupting your body’s own melatonin production.

Melatonin helps regulate your circadian rhythms, which regulate your sleep and wake schedule. It impacts REM (rapid eye movement) and stage 4 sleep. That’s the stage of rejuvenating sleep you need in order to think clearly, stay focused, repair muscle tissue, relieve pain, recharge your immune system, and stop the development of tumors. Stage 4 sleep is critical to good health!
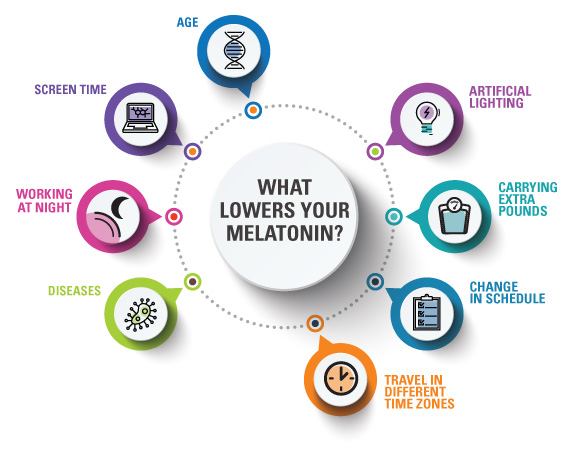 What Lowers Your Melatonin?
What Lowers Your Melatonin?In our modern world, we have a lot of threats to melatonin: light pollution, aging, shift work, screen time, and late nights. Over time, it adds up. Just two hours of continuous screen time depletes melatonin levels by 22 percent. After a while, these factors take a toll.
Younger people typically have about 8-10 times more naturally circulating melatonin at night than they do during the day. That makes sense, because sunlight depletes melatonin levels as part of our natural circadian rhythms. But older individuals may only have twice as much natural melatonin at night compared to daytime hours. That may sound like a lot, but it isn’t. In fact, many people experience declining melatonin levels as they age. To overcome the many threats to our natural melatonin levels, supplementation is a must for many of us.
The Miracle of Melatonin—Health Beyond Restorative Sleep
Start Taking Melatonin Tonight
There is a huge price to pay by denying our own circadian rhythms. As researchers have noted, we are really fighting against our own programming. Interestingly, moonlight—a reflected light—does not harm our circadian rhythms because it is the wrong wavelength to affect melatonin (yellow light). But blue lights from television, phones, nightlights, and security lights are literally poisonous to melatonin. Even the World Health Organization recognizes blue light at night as a Class II carcinogen. I believe that melatonin is, in many ways, like vitamin D—a critical component of health that has been here all along, but is finally becoming recognized for its incredible value. Start taking some tonight, and I can guarantee that it will make a major improvement in your life.
Melatonin Made Easy — Here’s What to Look For:
Melatonin is quickly metabolized by the body, so some supplemental forms can be completely cycled through in as little as two hours. If you haven’t noticed much disruption in your sleep at this point, that might be fine— just take a standard melatonin, like a 5 mg chewable for instance, about an hour or two before you go to bed.
Additionally, you may want sustained release benefits from melatonin, so consider looking for a form that slowly administers itself into your bloodstream over time as it breaks down in the digestive tract. This is the same form that is used in clinical research, because it helps reestablish circadian rhythms more efficiently and effectively.
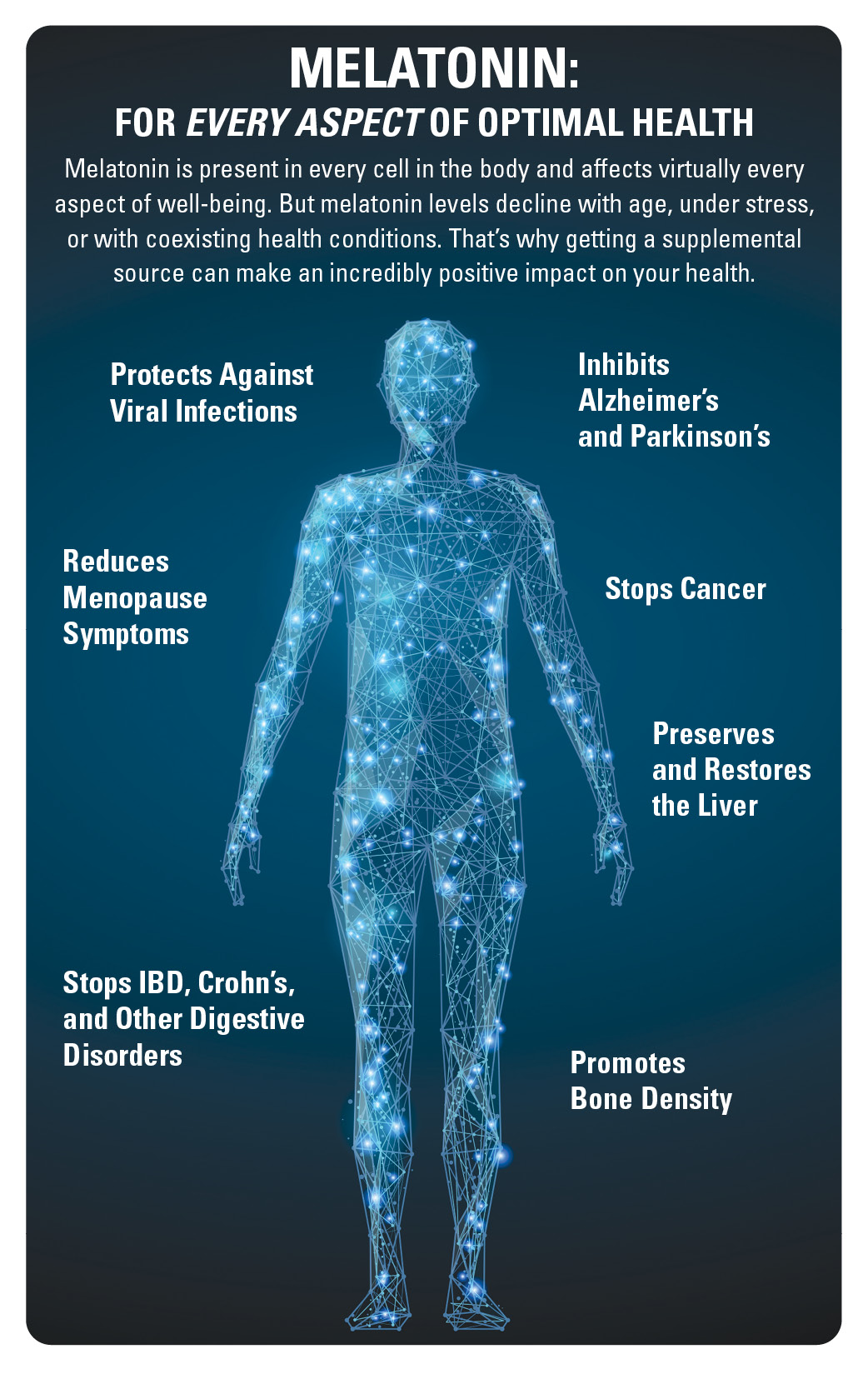 To get the full benefits of melatonin, I recommend using melatonin daily.
To get the full benefits of melatonin, I recommend using melatonin daily.